How to Read Sperm Analysis Report
Any condition in a man that affects the chances of getting the female partner pregnant is known as male infertility. The most common cause of male infertility is to do with the health of the sperm.
Male fertility is diagnosed through a number of tests, the most important being the semen analysis test. After collection, the semen sample is sent to a laboratory where it is assessed for various factors such as volume of semen, semen count, motility and morphology. Absence or low sperm numbers does not necessarily indicate that a man is absolutely infertile. It could point to a hindrance with the production or delivery of the sperm.
If you have had a semen analysis done recently, and received the report, you might be wondering what the numbers on the report mean. Let us look at some of the terms generally mentioned in the semen analysis report and what the healthy levels for each should be.
Semen Ejaculate Volume
On an average, a man produces 2 – 5 ml volume of semen on ejaculation. If the volume is low or absent, it could be due to the following reasons:
- Failed emission (inability to ejaculate)
- Incomplete collection (partial collection of the semen)
- Problems or absence of the duct that carries the spermatozoa.
- Short abstinence interval (Engaging in sexual intercourse too frequently.)
Sperm Concentration
Spermatozoa concentration should typically be a minimum of 15 million per ml. If the count is lower than this, it is called oligospermia where as if no sperms are present in the semen, it is termed azoospermia. If the sperm concentration is below 5 million/ml, it is considered severely low. Sperm count can fluctuate on a daily basis and is also affected by abstinence of sexual intercourse.
Sperm Motility
Sperm motility (movement) is as important as sperm count. Motility can be further divided into total motility (any kind of movement) and progressive motility (forward movement). Healthy sperm must have a fast, forward movement. This allows the sperm to swim to their destination, which is the female reproductive tract, and fertilize the egg. Over 50% sperm motility provides a better chance of pregnancy. If the motility is lower than normal, it is termed asthenospermia.
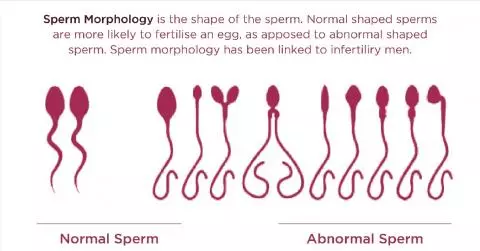
Sperm Morphology
Sperm morphology refers to the shape and size (appearance) of the sperms. The semen sample is examined to check what percentage of the sperms has a normal shape. The shape of the sperm’s head, body and tail are taken into account. Normally, the sperm should have an oval head and an extended tail. If the sperm is misshapen, it might indicate that the health of the sperm has been affected by exposure to toxins, chemicals or other problems. Even if the sperm sample has 12% normal sperms, it is considered normal. Higher percentage of abnormal sperms is termed teratospermia.
What Abnormal Sperm Results Indicate
If your semen analysis report shows any irregularities, your fertility expert might recommend another semen analysis after four to six weeks. If the report still shows abnormalities after the second analysis, other tests might be conducted to look for underlying problems. Some cases can be treated with minor alterations to lifestyle or medication. Latest developments in reproductive medicine have made it possible to treat many infertility issues. Consult an andrologist to understand your semen analysis report in detail and to receive the best infertility treatment available.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF