How PCOS is Related to Ovulation Disorders: Understanding the Connection
PCOS or Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is one of the most common causes of infertility. This is characterized by hormonal imbalances and problems with metabolism. PCOS is not a disease but is a collection of symptoms caused by higher than normal levels of male hormones and lowered levels of female hormones.
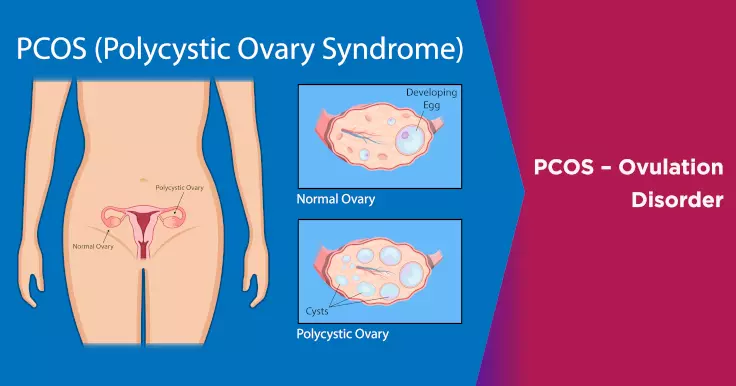
How PCOS Related to Ovulation Disorder
A woman’s ovaries contain multiple eggs. Each month, a few of these eggs begin to develop until gradually one becomes dominant and mature. This egg is then released to set off the menstrual cycle. If the egg is not fertilized, it is discharged from the ovaries in the form of a period.
In the case of women with PCOS, the ovaries do not get a signal from the pituitary gland to produce the hormones needed for eggs to mature. This may be because of high insulin levels associated with PCOS. The follicles containing eggs that do start to mature stop when the hormones are not released. Since the eggs have not matured fully, they cannot be released. This leads to the formation of small cysts on the outer rim of the ovaries. Thus, a woman with PCOS may not ovulate regularly. This can lead to irregular periods of skipped periods. Without an egg to be fertilized, natural conception is very difficult.
Treatment for PCOS
An ultrasound that shows the presence of these cysts is one of the ways a PCOS diagnosis is confirmed. Though the exact cause of the syndrome may is not clear, PCOS can be managed and controlled with medication and lifestyle changes. There is no standard form of treatment for PCOS and treatment must always be prescribed on a case to case basis. Keeping PCOS and its symptoms under control can have a significantly positive effect on fertility. A healthy diet and exercise are the keys to achieving this.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF