Everything You Need to Know About Scrotal Ultrasound
The scrotal ultrasound is one of the primary methods of evaluating any disorders of the testicles, the epididymis, and other scrotal structures. Generally recommended by an andrologist, a scrotal ultrasound can be helpful in determining the cause of infertility in males as well. It is a fairly simple procedure, but it can reveal valuable information about a male’s reproductive health. Naturally, a person who has been recommended to get a scrotal ultrasound may feel curious to know about the procedure. Here, you can learn everything you need to know about scrotal ultrasound and what to expect during this test.
What Is a Scrotal Ultrasound?
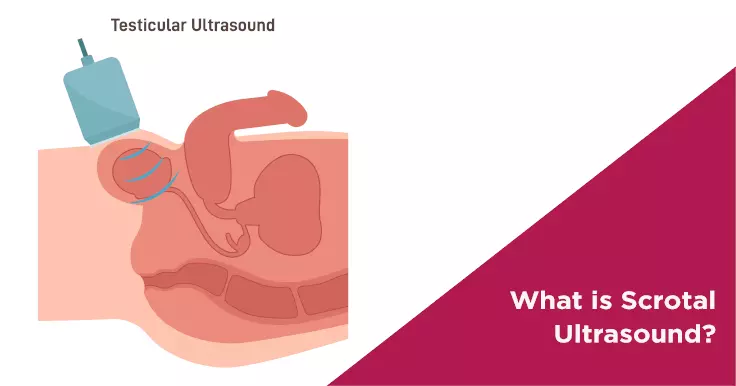
Scrotal ultrasound, also known as testicular ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging test that is used to obtain images of the testicles and surrounding tissue. This is a non-invasive test that can help your andrologist diagnose medical conditions affecting the organs contained in the scrotum.
The scrotum is a skin-covered, muscular sac, and it is located at the base of the penis. Scrotum is essentially a sac that holds the testicles of a male. Testicles are an important part of the male reproductive system that are responsible for producing testosterone (one of the male sex hormones) and sperm. The scrotum contains epididymis, blood vessels, and vas deferens (a coiled tube that carries the sperm out of the testes).
Testicular ultrasound is used to examine the testicles and other scrotal structures. The results of the ultrasound procedure are visible on a monitor, which aids the technician in properly examine the scrotal structures. Oftentimes, scrotal ultrasound is used to determine the cause of enlargement of the testicles or pain in the testicles.
The testicular ultrasound is a safe, painless procedure that captures the inside of the scrotum using sound waves. High-frequency sound waves travel through the gel into the body from the small probe.
Purpose of the Scrotal Ultrasound
The scrotal ultrasound is typically used to:
- Diagnose the cause of scrotal pain that is commonly caused by epididymitis
- Check for absent or undescended testicles
- Check for twisting of the spermatic cord or testicular torsion that can be caused by some abnormalities during foetal development
- Determine the location and condition of the mass or lump found in the scrotum during a physical examination
- Evaluate the reason for infertility that may be caused by conditions such as varicocele
- Measure the testicular size
- Check the testicles of men with a history of testicular cancers or infections
- Serve as a guide during needle biopsy for certain testicular masses
Why Do I Need a Scrotal Ultrasound?
Your doctor will recommend a scrotal ultrasound if you are experiencing any pain, swelling, or other concerning symptoms related to your scrotum. The scrotal ultrasound can help diagnose the following health problems:
Testicular Torsion
If there is a sudden onset of pain in a sensitive area like the scrotum, it is usually a cause for concern and shouldn’t be ignored. Testicular torsion is a condition in which the spermatic cord, which supplies blood to the testicle) becomes twisted and leads to sudden and severe pain in one testicle.
This is a serious medical condition that required immediate medical attention to avoid the death of the tissue of the affected testicle as it is not receive any blood supply. Surgery is often required to treat the condition and prevent further damage to the testicle.
Testicular Lumps
A testicular lump revealed in a physical examination may be a cancerous tumour. The doctors recommend a scrotal ultrasound if they suspect any masses or lumps inside the scrotum. The result of a scrotal ultrasound can help the doctor evaluate the lump for its size, location, and other parameters. If the lump appears to be solid in the ultrasound images, it can be cancerous, but if the lump is filled with fluid, it is most likely harmless.
Epididymitis
Epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis) can be the cause of pain in your scrotum as it is one of the most common causes of pain in that area. Epididymitis can lead to fluid build-up around the testicle and cause swelling or lump formation. However, this condition is easily treatable with the help of antibiotics as it is often caused by an infection.
Infertility
A scrotal ultrasound may also be a part of an infertility assessment that you may require in order to proceed with your fertility treatment. Since the testicles are responsible for making and storing sperm, any problem affecting this area can cause infertility. Thus, it is important to examine the area properly to understand the cause of infertility for a male.
Undescended Testicles
Scrotal ultrasound is also an excellent tool to detect an absent or undescended testicle. An undescended testicle is common in young males. When a male foetus is developing inside the womb, his testicles ideally move downwards to sit outside the body below his penis from the abdomen. This process usually happens before the baby is delivered, but it may take up to 6 months after birth to happen for a male infant.
In case the baby boy’s testicles don’t descend on their own within 6 months of his life, it is essential to consult a specialist. The doctor will likely recommend a scrotal ultrasound to detect the presence and location of the undescended testicles. To treat undescended testicles, surgery may be required to manually move the testicles down to sit in the correct position.
How Is the Scrotal Ultrasound Performed?
An outpatient procedure, the scrotal ultrasound can be performed in a doctor’s office or a hospital’s radiology department. The entire scrotal ultrasound procedure may take anywhere from 20 to 30 minutes.
A scrotal ultrasound starts with posting the patient on the examination table in a proper manner. For this, the patient will be asked to lie down on his back while spreading the legs apart. The doctor will examine the scrotum manually after positioning the penis towards the abdomen and covering it with a cloth. The scrotum will be raised by the examiner using a rolled-up towel or wide strips of tape. During the procedure, the patient needs to remain completely still in order to provide a better view for the examiner.
Afterwards, a water-soluble gel is smeared on the scrotum to allow the proper transmission of sound waves. The gel also helps the ultrasound probe move over the scrotum in a smooth manner. The technologist then moves a handheld probe or transducer back and forth on the scrotum to exams the scrotal structure and organs inside it from various angles. The wave transmitted by the machine reflects off the areas in the scrotum and creates an image. The radiologist will try to get the clearest visuals possible during the procedure, which are also recorded on a film or tapped as a video. Each side of the scrotum is examined using the ultrasound transducer.
After the completion of the test, the examiner wipes off the gel from the scrotal skin. You can resume your normal activities and continue going about your day if you are not experiencing any excruciating pain. There is no recovery time required for a scrotal ultrasound.
How to Prepare for the Scrotal Ultrasound Test?
Before performing the scrotal ultrasound, the patient will be asked to change and wear the hospital robe. No other preparation from the patient’s end is required.
You don’t need to change your medication or diet in any manner to prepare for this test. People going for ultrasounds are usually asked to maintain a full bladder or avoid eating anything. However, you don’t typically need to do any preparation for a scrotal ultrasound.
What Happens During Scrotal Ultrasound?
During the testicular ultrasound procedure, you may feel a certain level of discomfort if you have tenderness in your scrotum due to the pressure of the transducer probe.
The whole procedure is relatively simple; it requires the patient to change into a hospital gown and lay on the examination table so that the radiologist can perform the test.
Interpreting Scrotal Ultrasound Test Results
The results of a scrotal ultrasound are usually available soon after the procedure and the patient can consult his doctor about his results right after the procedure. In some cases, a radiologist may study the test results before preparing the results for the doctor to evaluate.
After the images are formed, the physician will review them closely. If the testicles and other areas of the scrotum appear normal in size and shape, then it is considered as a normal result. An abnormal result could also be due to the following:
- Collection of several tiny veins or varicocele
- Inflammation
- Benign cyst or mass
- Blocked blood flow due to twisting of the testicle or testicular torsion
- Testicular tumour
- Shrinkage of the testicle or testicular atrophy
- Abscess or pocket of puss due to infection
In case of an abnormal finding in the scrotal ultrasound, your doctor may recommend further diagnostic tests, especially if a tumour was detected during the procedure.
Risks of Scrotal Ultrasound
Scrotal ultrasound is a non-invasive and safe procedure that doesn’t put you at risk for any health concerns. There are no known risks of scrotal ultrasound as the procedure doesn’t use radiation and no incisions are required. Thus, you don’t need to worry about any side-effects from the scrotal ultrasound.
However, if you are getting a scrotal ultrasound due to pain in the area, you may experience an increase in the pain during the diagnostic procedure or increased discomfort.
Considerations of Scrotal Ultrasound
A Doppler ultrasound may be required in certain cases to evaluate the scrotum, especially if the male has testicular torsion causing the blood flow to the twister testicle. Doppler ultrasound employs the Doppler effect to examine the movement of tissue and bodily fluids inside the body, including blood.
Summing Up
A testicular ultrasound is used to diagnose a range of health problems related to the male reproductive system, including varicocele, testicular cancer, epididymitis, and testicular torsion. Learning about the procedure may help calm your nerves and give you an idea of what to expect from it. Hopefully, the information mentioned above has helped you understand the low-risk procedure of a scrotal ultrasound.
If you wish to speak to a skilled andrologist, consider booking an appointment with Nova IVF Fertility near you. We specialise in fertility treatment and have helped numerous people over the last few decades build their families.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF