Hypospadias Causes and Its Effect on Male Reproductive Health
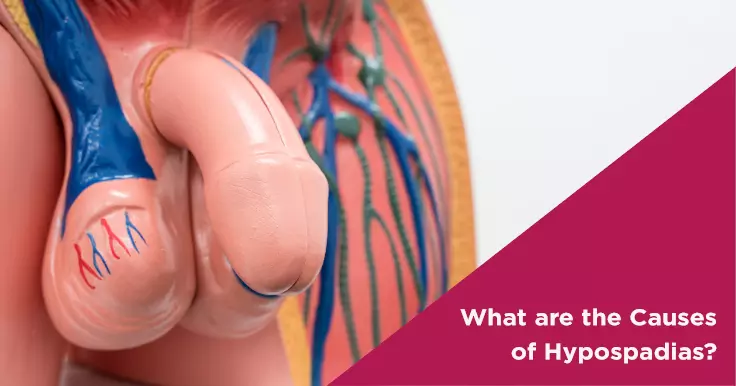
Hypospadias is a birth defect in which the opening of the urethra is on the underside of the penis instead of being located on the tip. It is a common congenital condition which is found in one in every 200 male infants and can be corrected by surgery.
Normally detected at birth, this condition can lead to issues in the future related to fertility and urination and hence needs to be corrected. Hypospadias is usually diagnosed at birth upon close examination. However, some cases may be subtle, and the diagnosis may not occur immediately after birth. It can affect the infant's hygiene and also make it harder to detect symptoms of rashes or infections.
What are the Causes of Hypospadias?
Hypospadias is a development issue and often does not affect any other organs. The formation of the urethra and the foreskin along with the meatus in a male foetus is due to the stimulation of certain hormones. When a malfunction occurs in the hormonal balance, the urethra tends to develop abnormally, leading to hypospadias.
The exact cause of this condition remains unknown. However, there are certain causes that are attributed to hypospadias:
- Genetics: A family history of the condition makes the infant more prone to acquiring this condition.
- Fertility treatments: Hormone therapies that are used to better the chances of fertilisation can increase the chances of hypospadias in an infant.
- Maternal factors: The age and weight of the mother can influence the chances of an infant being born with hypospadias. A history of diabetes for the parent, or being of age over 35, can increase the chances.
- Pesticide exposure: Exposure of the mother to pesticides or smoking.
- Premature birth of the baby can also cause this condition.
To reduce the chances of an infant being born with hypospadias, the mother can protect herself from exposure to alcohol and drinking during the pregnancy. Leading a healthy lifestyle along with a healthy diet can prevent this condition to an extent.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF