Ovarian Cancer

Ovarian cancer has very few distinct symptoms and hence is often difficult to diagnose. In fact, only about 20% of ovarian cancer cases are diagnosed in the early stages. An early diagnosis is key to treating ovarian cancer.
Thus, it is important to learn about the disease to understand the risk factors, your likelihood of developing this disease, and how it is treated. This is a comprehensive guide to help you understand ovarian cancer stages, symptoms, treatment options, and more.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer
Cancer that begins in the ovaries or cells in the distal end of a woman's fallopian tubes is known as ovarian cancer. It is marked by the rapid, uncontrolled multiplication of mutated cells that have a much longer lifespan than normal ones. As a result, they lead to growths known as tumours.
Unfortunately, most cases of ovarian cancer are diagnosed very late after the tumour has spread to other parts of the abdomen as it is usually quite hard to detect. Women with a family history of ovarian cancer have a high risk of suffering from this type of cancer and hence must get regular check-ups.
It can affect one or both ovaries and is caused by a genetic mutation. Ovarian cancer is marked by the abnormal growth of cells in the ovaries because of a genetic mutation. These cells then begin multiplying rapidly. Since they live for much longer than normal cells, they turn into tumours. As the disease progresses, the mutated cells may spread from the ovaries to other organs.
Types of Ovarian Cancer
Typically, there are 3 types of ovarian cancer. These are categorised on the basis or the type of cell where the cancer mutation originates.
- Epithelial Tumours: Tumours that originate in the thin tissue layer surrounding the outside of the ovaries are known as epithelial tumours. This is the most common type of ovarian cancer and is seen in 90% of such cancer cases.
- Stromal Tumours: This is a rare type of ovarian cancer that originates in the tissue that houses hormone-producing cells. Young women have a higher risk of this type of cancer as compared to post-menopausal women.
- Germ Cell Tumours: This also usually affects younger women. It originates in the egg-producing cells of the ovaries. Germ cell tumours are of many types. The most common amongst these are dysgerminomas, teratomas, choriocarcinomas and endodermal sinus tumours.
What Causes Ovarian Cancer?
Genetic mutations are the primary ovarian cancer causes. A woman with a family history of ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, breast cancer or colorectal cancer has a high risk of ovarian cancer. This is because she may inherit mutated genes associated with these types of cancer from her parents. Some of the inherited genetic mutations that can cause ovarian cancer include BRCA1, BRCA2, MLH1 & 3, MSH 2 & 6, PTEN, TGFBR2, STK11, PMS 1 & 2 and MUTYH.
Ovarian Cancer Risk Factors
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown but there are several factors that may increase a woman's risk of developing cancerous tumours in the ovaries, including the following:
- Reproductive Health: Women who start menstruating before the age of 12 years have a higher risk of this type of cancer. Similarly, women who reach menopause after the age of 50 years also have a high risk. Having your first child after you reach the age of 30 years or not having children at all is also considered a risk factor. Taking hormonal replacement therapy may increase the risk of ovarian cancer but this is quite rare.
Women who start menstruating before the age of 12 years have a higher risk of this type of cancer. Similarly, women who reach menopause after On the other hand, oral birth control pills, getting your tubes tied and breastfeeding can reduce the risk of this type of cancer. - Ethnicity and Age: Ovarian cancer is rarely seen amongst women who have not yet reached menopause. Ovarian cancer can occur at any age. However, it is more commonly seen amongst women between the ages of 50 and 60 years. Most cases are diagnosed when a woman has crossed the age of 60 years.
When it comes to ethnicity, non-Hispanic white women are considered to have the highest risk of this cancer. - Body Size: Obesity is one of the major risk factors associated with ovarian cancer. It has also been observed that women who are taller than 5 feet 8 inches have a higher risk of this type of cancer.
- Family Medical History: Women who have a family history of ovarian cancer and breast cancer have a higher risk of suffering from ovarian cancer themselves. This is because some types of ovarian cancer may be caused by genetic mutations that are inherited from one's parents. The BRCA1 and the BRCA2 are two such genes. These genes also increase a woman's risk of developing breast cancer. Similarly, genetic mutations associated with the Lynch syndrome can also increase a woman's risk of ovarian cancer.
- Oestrogen Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk of ovarian cancer especially if the hormone is administered in large doses.
- Menstruation and Menopause: Most women start menstruating in their early teenage years and reach menopause in their 40s. Women who begin menstruating early as well as those who reach menopause later than normal may have a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
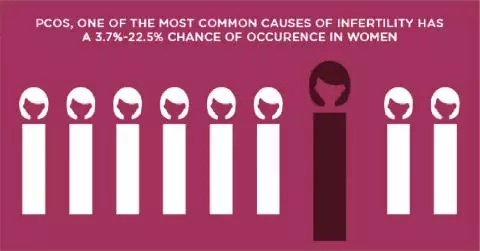
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer
- Endometriosis
- PTEN Tumour Hamartoma Syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- MUTYH-Associated Polyposis
Ovarian Cancer Stages
There are 4 stages of ovarian cancer:
- Stage 1: In the initial stages, the cancer affects only the ovaries.
- Stage 2: In this stage, the condition spreads from the ovaries to other organs in the pelvic cavity.
- Stage 3: In this stage, tumour spreads to abdominal lymph nodes and the abdominal lining.
- Stage 4: In the last stage, ovarian cancer spreads to other parts of the body outside the pelvic cavity.
Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
It is quite easy to overlook the early signs of ovarian cancer as they are very similar to signs of other common illnesses. These symptoms do not usually persist and may come and go. Common symptoms associated with ovarian cancer include:
- Pain or pressure in the abdomen
- Bloating of the abdomen
- Feeling very full after eating even just a little bit
- Trouble eating food
- An increased frequency in the urge to urinate
- An increase in the amount of urine passed
- Frequent indigestion
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Heartburn
- Pain in the back
- Constipation
- Pain while having sexual intercourse
- Irregular periods
- Heavier than normal menstrual bleeding
- Dermatomyositis, which is a rare disease that can cause weakness of the muscle, rashes, and inflammation in the muscle tissue.
Women who are experiencing these symptoms don’t necessarily have ovarian cancer as these symptoms can also be caused by other diseases. However, if they persist over a longer period of time or are severe in intensity, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
It is also important to get regular check-ups if you have a personal history of cancer or a family history of ovarian or breast cancer. This is because the genetic mutations associated with ovarian cancer may be inherited from either parent. In such cases, ask your doctor about screening tests for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
Due to negligible ovarian cancer symptoms noticeable in the initial stages of this condition, it is often diagnosed in later stages. However, if you suspect you might have ovarian cancer, testing for it begins with a physical examination. The doctor will check your pelvis for an enlarged ovary as well as the presence of fluid in the abdomen. There are primarily two ways to diagnose ovarian cancer:
- Imaging Testing for Ovarian Cancer: In addition to a physical examination, a few other additional imaging tests may also be required. These tests take pictures of the inside of the pelvic cavity. Several types of imaging tests may be used to diagnose ovarian cancer; these include:
- Transvaginal (internal) or regular (external) ultrasounds
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Barium enema x-ray
- Colonoscopy
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
- X-ray
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
- Ovarian Biopsy: A biopsy is also a part of the ovarian cancer diagnosis. This involves taking a small sample of cells from the affected areas and examining them under a microscope. This may be performed after a tumour is removed or by removing a few cells with an injection that is guided by a CT scan or ultrasound.
Ovarian Cancer Treatment Options
Treatment of ovarian cancer depends on the stage of cancer it is diagnosed at and the patient's overall physical and mental health. In many cases, two or more different types of treatment may be used together. The treatment includes:
- Surgery: Surgery to remove a tumour is usually the first step of treating ovarian cancer. The mass that is removed is then sent to a lab to be tested. If it is malignant, further treatment may be required to ensure that cancer does not recur. If the cancer is in its advanced stages and if the woman does not plan on having any children in the future, all the reproductive organs may be removed. The surgery is usually performed while the patient is under general anaesthesia and hospitalisation may be required for a few days after the procedure.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is often used for ovarian cancer treatment. This type of treatment may be used before or after surgery. It involves administering medication through an IV to kill the cancer cells in the body. In the case of ovarian cancer, these medicines may also be injected through an injection into the abdomen. If a tumour is very large, it is used before surgery to shrink a tumour. After the surgery, several cycles of chemotherapy may be given to remove all traces of the mutated cells.
- Radiation: Radiation is used for two purposes. After surgery to remove a tumour, it may be used to remove any remaining cancer cells. In the case of advanced ovarian cancer, radiation may be used to manage the symptoms associated with it. For example, by shrinking the size of a tumour, it can help reduce abdominal pain. The process of receiving radiation treatment is similar to having an X-ray. Like chemotherapy, radiation may also be given in cycles. This type of treatment may also be used to address recurring cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: This is a relatively new form of therapy for ovarian cancer. It involves administering medication that targets the affected cells without causing any damage to the other healthy cells. These medicines work towards keeping the mutated cells from multiplying. It may be administered orally or through an IV.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy may be used to treat certain types of ovarian cancer such as stromal tumours. It is rarely used to treat epithelial ovarian cancer. This type of treatment is aimed at reducing the oestrogen levels and in turn keeping the cancer cells from multiplying.
In addition, there are several clinical trials also being conducted around the world to find new ways of treating ovarian cancer. In the case of clinical trials, it is important to remember that it is not necessary for the trial to be successful and that there is only a 50% chance that you will be given the new drug.
Living with Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer treatment may remove or destroy the cancerous cells and offer hope for some people. It is extremely important to follow through with the recommended treatment plan with patience. People who have recovered from ovarian cancer often find themselves worrying about it returning, which is a possibility.
If you are going through ovarian cancer treatment or have completed it, your doctor will likely recommend a follow-up care plan, make sure to follow that.
The diagnosis of ovarian cancer can be as stressful as the treatment itself for some people. Additionally, dealing with the side-effect of ovarian cancer treatment can be disheartening and feel like a burden sometimes. Thus, women diagnosed with ovarian cancer are advised to keep a tab on their mental health and seek help if needed.
Ovarian Cancer Prevention and Early Detection
One cannot prevent ovarian cancer completely, but the risk can be reduced in some cases. Regular pelvic exams play a vital role in reducing the risk and early detection of ovarian cancer. Taking oral contraceptives can reduce the risk of this type of cancer. In the case of women with a family history of such cancer, you may choose to undergo genetic testing or have your ovaries removed.
Advocacy and Support Networks
There are numerous resources and organisations that offer support and advocacy for those affected by ovarian cancer. For gathering information about ovarian cancer and seeking support, consider the following resources:
- Indian Cancer Society (ICS)
- World Ovarian Cancer Coalition
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (ICAR) by WHO
- UHAPO
- Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance (OCRA)
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (ACOG)
Research and Future Directions
Here is a list of latest research in the field of ovarian cancer that you may find interesting:
- Advances in ovarian cancer therapy
- Recent progress in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer
- Screening for Ovarian Cancer
- Patterns and Progress in Ovarian Cancer Over 14 years
- Ovarian cancer: Survival and treatment differences by age
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF