Understanding the Risks of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)

Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome is a condition where the woman’s ovaries swell up as a result of medication. It may also be accompanied by fluid retention in the abdomen. The swelling of the ovaries causes the blood vessels to leak fluid into the abdominal cavity. This can cause pain, discomfort and a host of other symptoms. Symptoms caused by OHSS usually heal on their own. However, severe cases of OHSS may require hospitalization.
Irregular ovulation is a common cause of infertility. In such cases, fertility treatment may be prescribed to stimulate the production and release of eggs by the ovaries. This usually takes the form of hormone-based medication. Taking hormone medication for an extended period of time can have several side effects. Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome is one such condition.
Is OHSS Common?
Mild OHSS is considered quite a normal reaction to hormone medication. This is seen in almost 20-35% of women who undergo IVF. In such cases, the symptoms usually are relieved within a week. However, if the woman gets pregnant, the symptoms may last for several weeks and may even worsen. This is seen especially in the case of multiple pregnancies.
Moderate OHSS affects 3-6% of women who undergo IVF treatment. Severe OHSS is quite rare. Only 1-3% of women undergoing IVF have such symptoms. In such cases, it is important to immediately seek medical attention.
Types of OHSS
OHSS is categorized into four types: mild, moderate, severe, and critical.
- Mild OHSS: Enlarged ovaries, nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhoea are the common symptoms
- Moderate OHSS: In this case fluid builds up inside the abdomen, leading to abdominal pain and vomiting
- Severe OHSS: Extreme thirst, dehydration, pain in the chest, and dark colored urine are symptoms of the severe form of OHSS
- Critical OHSS: Common symptoms of critical OHSS include enlarged ovary, renal failure, ascites, pleural effusion etc.
How is OHSS cause?
Many cases of infertility are caused by irregular ovulation or the absence of ovulation. This can be treated with hormone medication. The medication is used to stimulate the ovaries to the production and release of healthy eggs. In some cases, women taking injectable hormone medication may develop multiple eggs or hyperstimulation. This is characterised by the swelling of ovaries. In rare cases, it may occur even if one does not undergo fertility treatment. Most of the time women undergoing IVF or IUI treatment are taking these kinds of medication.
Inflammation in the ovaries, in turn, triggers the leakage of fluids from blood vessels. It gives rise to symptoms that may be classified as mild, moderate and severe. Mild symptoms are considered a normal reaction in the case of fertility treatment such as IVF.
Almost 20-35% of women who are treated with IVF develop mild symptoms of OHSS. These symptoms usually disappear after a week. However, if a woman gets pregnant during this time, the symptoms may stay for longer and may even worsen.
What are the Symptoms of OHSS?
Women who develop OHSS usually begin showing symptoms within 10 days of taking the medication. These symptoms are more commonly noted amongst women who take injectable medication as compared to those who take the medicine orally.
Symptoms of Mild to Moderate OHSS
These symptoms are usually not something to worry about. They include:
- Mild to moderate cramping and abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Tenderness in the pelvic area
- Sudden unexplained weight gain.
Symptoms of Severe OHSS
Severe OHSS is rare. This is seen only in about 1-3% of women who are treated for infertility with IVF. The symptoms can include:
- Severe abdominal cramping and pain
- Rapid weight gain. This can be as much as 15-20 kgs in 5-10 days
- Persistent nausea
- Vomiting
- Reduced urge to urinate
- Dark colored urine
- Shortness of breath
- Tight and enlarged abdomen
- Pain in the calves
- Blood clots in the legs
What are the Risks of OHSS?
If women are consuming fertility drugs to stimulate the development and production of eggs in the ovaries, there are high chances that they might be affected with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). The fertility drugs are generally taken by women undergoing intrauterine insemination or in vitro fertilisation.
Women taking a high dose of hormone medications are generally prone to OHSS where the ovaries are enlarged. Other symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, rapid weight gain, and breathlessness.
The Risks of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome Include:
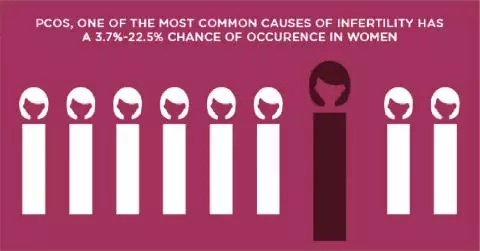
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): This condition includes the presence of numerous cysts in the ovaries. Major symptoms of PCOS are irregular menses, excess hair growth, and unusual weight gain or weight loss
- A steep increase in the estrogen hormone levels
- The large number of follicles
- Low body weight
- Women aged below 35
- Previous diagnosis of OHSS
OHSS is mainly caused due to increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the body. Sometimes, women attempting to get pregnant are given a high dose of this hormone, which triggers an abnormal reaction of ovarian blood vessels, which causes them to start leaking fluid. This fluid causes swelling of the ovaries and sometimes, a large amount of this fluid flows inside the abdomen. The health condition of women under hCG shots worsens if they get pregnant since pregnancy also causes their body to produce high levels of hCG.
Who Is At Risk of OHSS
Risk factors for developing moderate to severe symptoms of OHSS include:
- History of experiencing OHSS before
- Medication being administered through injections
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Low body weight
- High levels of oestrogen before receiving hormone medication
- High follicle count
- Those who suffer from migraines
- Age less than 35 years
Can OHSS be prevented?
Doctors may advise taking certain medication along with hormonal treatment to reduce the risk of OHSS. Taking medication orally can also reduce the risk of this condition. Resting and drinking electrolyte balanced fluids instead of water can also reduce the risk of OHSS. Doing Embryo Transfer in the later cycle is also suggested.
When Should You Consult
OHSS is usually a self-limiting problem. But till it disappears one should be under supervision of a treating doctor. In the case of mild symptoms, there is usually no need to worry. However, you must be aware of the symptoms and keep an eye to see if they worsen. The doctor may advise you to keep a tab on your weight so as to check for the weight increase. One should take light food and drink plenty of liquid and ambulate.
In the case of severe OHSS, you should consult a doctor immediately. This is potentially dangerous and hospitalization may be required. In some cases, the IVF cycle may need to be stopped and the woman’s embryo may be frozen so that they can be used for a later cycle. Usually once period start effect of OHSS is washed off from the body.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF