What Are the Symptoms of Hypospadias?
Hypospadias is a congenital condition that occurs in newborns. In the condition, the opening of the urethra is located beneath the penis instead of on the head of the tip. This condition can lead to issues in the future such as infertility due to the sperm not reaching the egg. It can also cause urination problems and hence should be treated at the earliest.
A minor surgery is done to correct the position and relocate it in its accurate position and prevent future problems. Hypospadias is usually diagnosed after birth and in some rare cases, a few months after. This is due to the symptoms being subtle during the time of birth. This is a development condition and hence does not affect any other organs.
What are the Symptoms?
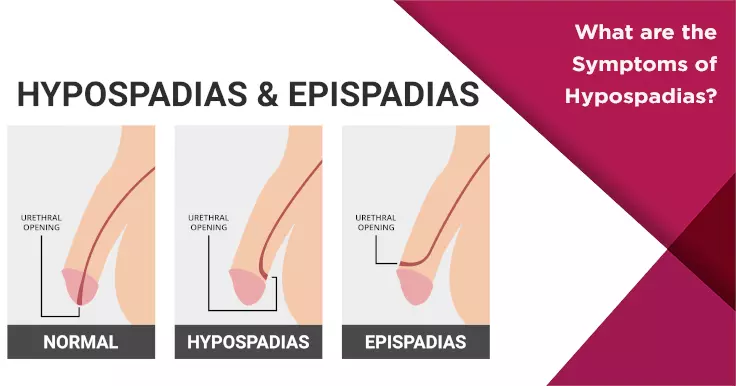
Hypospadias causes the opening of the urethra to be wrongly located on the underside of the shaft of the penis. In rare cases, it can be located beneath the scrotum as well. Based on its positioning it can be classified as:
- Anterior (located near the tip of the penis)
- Middle (midway up the penis)
- Posterior (at the scrotum or perineum)
There are various symptoms of hypospadias in an infant that can point towards this condition. They are listed below:
- Abnormal appearance of the tip of the penis
- The opening of the urethra away from the accurate positioning
- A curve on the penis (downwards) called chordee
- Only the top half of the penis gets covered by the foreskin leading to having a hooded appearance of the penis (partial development of foreskin)
- Abnormal urination (spraying)
Hypospadias can be identified by doctors upon examination. In cases where the signs are subtle, this condition can go undetectable for a few months. Infants with mild hypospadias can have no symptoms as well. Factors such as family history, maternal health, premature birth and exposure to chemicals and pesticides during pregnancy can all lead to hypospadias.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF