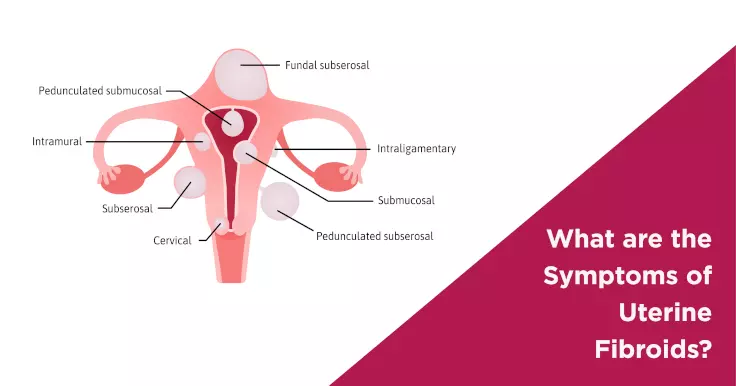
Fibroids are compact tumors made up of fibrous connective tissues and smooth muscle cells that develop in the uterus of a female. Around 30-77% of women in the childbearing age are diagnosed with fibroids as they are prone to uterine fibroids from menarche up until menopause.
Fibroids are generally known as fibromas, uterine myomas, or leiomyomas. In many cases, fibroids are non-cancerous or benign and do not increase the risk for uterine cancer in a woman; but a rare and cancerous version of uterine fibroids termed leiomyosarcomas can sometimes develop in a female's body. Women can have one to several fibroids in their uterus.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Although the main reason for fibroid formation in a woman's uterus is unknown, researchers believe that they develop from aberrant muscle cells of the uterus that tend to multiply on a large scale under the influence of estrogen. The main symptoms of uterine fibroids are given below:
- Heavy bleeding, including blood clots during or between menses
- Severe pain in the lower back or pelvic area
- Severe cramps during menstruation
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Frequent urination
- Long menstrual cycle
- The feeling of fullness or pressure in the lower abdominal area
- Enlargement or swelling in the abdominal area
These symptoms show up depending on the number of fibroids present in the uterus, along with their size and location. In case a woman has very small fibroids and is going through her menopause, she may never have noticed the symptoms. The major reason for this is the drop in the levels of estrogen and progesterone, hormones that support fibroid growth, in the body during menopause. And because of this reason, the fibroids may even shrink during or post-menopause.
In extremely rare cases, fibroids lead to infertility in women. If they are located at the submucosal position, they hamper the embryo implantation in the uterus and, leaving a woman incapable of getting pregnant.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF