Women who have fertility issues may not have the ability to produce good quality eggs to be used for IVF treatment. Egg donation process is a beacon of hope for such women. Women who are fertile can opt for egg donation to help such individuals fulfil their dreams of building a family without impacting their own fertility and a rewarding experience of knowing you've played a crucial role in someone’s journey; you will also receive financial compensation for your generous contribution.
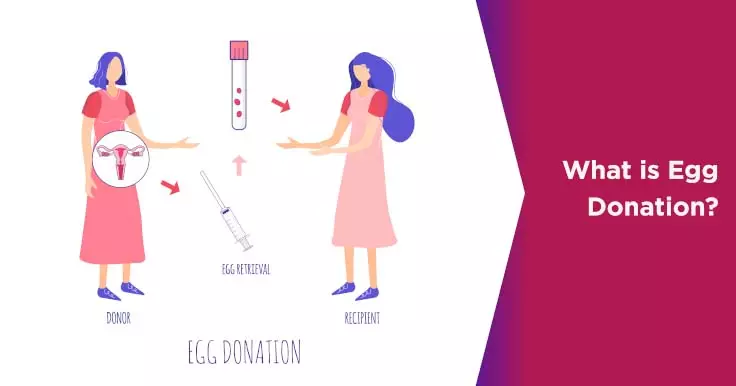
Egg donation is one of the ways to perform the IVF fertility treatment. The egg donation procedure typically involves the removal of mature eggs from the donor, fertilisation of these eggs, and transfer of 1 or 2 embryos in the recipient’s womb. This is a guide to help anyone curious about the egg donation process understand it better and make a well-informed decision if they want to opt for it or not.
What Is Egg Donation?
Egg donation is a method of assisted reproduction in which a woman donates her eggs (oocytes) which are used to help another woman have a baby. In some cases, the intended mother carries the donated egg in her own womb, and in other cases a surrogate may be brought in to carry the embryo. Donor eggs may be combined with the male partner's sperm or with donor sperm for fertilisation.
On an average, about 5-24 eggs can be retrieved in an IVF cycle according to a 2017 study. This number largely depends on the health and age of the donor and other guidelines followed by the clinic. The donor is compensated for her efforts for each donation depending on various factors, which may include the number of eggs retrieved and the quality of those eggs.
How Does Egg Donation Work? Who Uses Egg Donation?
Infertility is more common than people think. Egg donation is a key player in helping people who are experiencing infertility build their family. By donating an egg, a female can have a lasting impact on someone’s life. Without the volunteer efforts of eligible women, such couples may not be able to have their own family.
Donor Egg IVF is also an appropriate option for women who are unable to conceive with their own eggs provided there is no contraindication to carrying a pregnancy. The indications for donor egg IVF are as follows:
- Advanced age (women who are 42 years or older)
- Diminished ovarian reserve
- Premature ovarian failure either unexplained or due to autoimmune disorders
- Chemotherapy or surgical menopause
Women who carry a genetic mutation will also be appropriate candidates for IVF with donor egg.
What Are the Requirements for Egg Donation? Who Are the Egg Donors?
Egg donation, as per the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) guidelines is an anonymous process. The egg donors are young and healthy women, usually having at least one child of their own. They undergo a complete medical and psychological evaluation and are screened for infectious diseases like HIV and Hepatitis. All tests prescribed by the ICMR are performed and guidelines laid down by the ICMR are strictly adhered to. An egg donor is recruited into the program, only after the screening process and legal paperwork is complete.
IVF With Donor Eggs: Step-By-Step Process
Are you thinking about what does the donor egg IVF procedure involve? Here is a step-by-step guide to explain the egg donation process with respect to IVF treatment:
Step 1: Screening of Donors and Matching with Recipient
The initial phases of IVF cycle with egg donor requires the donor to apply for the process and go through some screening tests. The donor usually goes through physical exams, blood tests, urine tests, gynaecological exams, psychological evaluation, and a consultation to collect their family medical history. After it is established that a donor is eligible to donate eggs, she will be matched with the recipient.
Step 2: Synchronising Selected Donor and Recipient’s Menstrual Cycle for Ovarian Stimulation
A donor egg IVF cycle requires the synchronisation of both, the egg donor's cycle and the recipient's cycle; the recipient here can be the intended mother or a surrogate. The fertility specialist will use medication to synchronise the egg donor's menstrual cycle with the recipient's cycle.
Usually, the recipient of the donor egg starts a prescription of oestradiol from the 2nd day of her menstrual cycle to prepare her uterus for the pregnancy. At the same time, the donor begins her medication for ovarian stimulation. In about 11-12 days, the donor's follicles will likely be ready for retrieval.
Step 3: Egg Retrieval and Fertilisation
The Egg retrieval is performed under anaesthesia with the help of ultrasound. On the same day, the intended father provides a fresh semen sample or donor sperms are used to fertilise the eggs. The gametes are fertilised in the embryology laboratory.
During this time around, the recipient is started on medication to support the implantation process.
Step 4: Embryo Transfer
After being under observation in the embryology lab, 1 or 2 embryos are transferred to the recipient’s womb as per the fertility specialist’s guidelines. Transfer of the embryo occurs on the 3rd or 5th day after retrieval. If there are any surplus embryos, they are usually frozen using cryopreservation for use in subsequent attempts if needed.
After about 1-2 weeks of embryo transfer, the recipient undergoes an at-home pregnancy test and a clinical pregnancy test to confirm the results of the procedure. If the recipient is pregnant with the transferred embryo, she carries on the pregnancy with appropriate medical care. If the implantation wasn’t successful, she will not be pregnant in this cycle, and the doctors will make another attempt with surplus embryos from previous egg retrieval.
What to Expect During the Egg Donation Procedure?
Since the egg donation process involves the transfer of the donor’s eggs to the intended parents, many biological and legal aspects of the procedure need to be sorted out beforehand. The fertility clinic is responsible for conducting the intensive selection process to find a suitable donor for the intended parents and carefully run through the tests and legal requirements to begin the treatment.
Additionally, egg donation involves manipulation of the donor’s menstrual cycle; thus, it naturally comes with certain side-effects. The medication used for ovarian stimulation can cause hot flashes, nausea, headaches, fatigue, mood swings, and body aches.
During the egg retrieval, the donor is sedated and unconscious. The side-effects of this part of the process involve cramping and vaginal bleeding or discharge for up to a few days after the retrieval.
Risks and Side Effects for the Donor
The egg donation procedure is considered to a generally safe process when a board-certified medical professional is closely examining the process. The egg donation process does not result in any long-term health risks or fertility issues, if you don’t develop rare complications during the treatment.
However, here is a list of some short-term risks that you need to know before donating eggs:
1. Pregnancy
There is a high chance that you may become pregnant if you engage in unprotected sexual intercourse during your medicated cycle to donate eggs.
2. Weight Gain
You may observe a temporary weight gain while on the medication for egg donation process.
3. Side-Effects of the Medication
Since the medication used for ovarian stimulation includes a lot of hormones, you may notice some temporary side-effects while taking them. Headaches, mood swings, fatigue, bloating, and nausea are some of the common side-effects of IVF medication.
4. Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
OHSS is a rare complication that usually surfaces about 3-9 days after you start fertility medication, but if left unchecked, it can become life-threatening. In this condition, the ovaries become enlarged and lead to symptoms like pain, nausea, and diarrhoea.
5. Ovarian Torsion
This is another risk of the egg donation process. Ovarian torsion involves the twisting of ovaries if they are swollen. Symptoms can include severe pain, and surgery is the recommended treatment option for this rare complication.
6. Infection
Like any surgical procedure, the process of egg retrieval invites a certain level of risk for infections. However, females who go through the egg retrieval process usually don’t get infected.
If you experience any severe or persistent side-effects, consult your fertility specialist immediately.
Success Factors for Egg Donation
Some of the factors that can influence the chances of live birth from IVF treatment using donor eggs include the following:
1. Aged Between 21 and 35
Generally, the egg donors are aged between 21 and 35 as this age group tends to produce high quality of eggs. These women also respond to the treatment well and deliver a high number of eggs for each cycle as compared to any other age group that is legally eligible to donate their eggs.
2. Low Chances of Genetic Disorders
Women who don’t have a high chance of developing genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis, are usually preferred for egg donation.
3. Good Overall Health
The overall health and well-being of the donor also plays a significant role in the quality and quantity of the eggs she can produce in a single treatment cycle.
In the End
The egg donation process includes numerous physical and psychological examinations, and it can involve mental, physical, and legal challenges. If you are thinking about egg donation, it is recommended that you conduct thorough research to understand the short- and long-term implications of your decision for you and your family.
If you opt for egg donation, it can be an incredibly rewarding experience emotionally and financially. You can consult with fertility specialists at Nova IVF Fertility to clarify any doubts about the process and make an informed decision.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF