What Is Hysteroscopy? Understand its Procedure
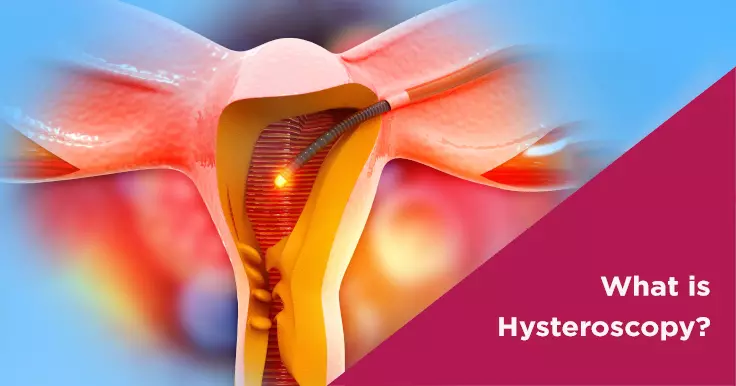
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that enables a doctor to closely examine the uterine cavity. It can be used to diagnose and treat problems of the uterus. A surgeon may carry out a hysteroscopy to:
- Investigate the cause of heavy bleeding during periods
- Check for fibroids or polyps(a non-cancerous growth in the womb)
- Inspect problems within the womb in case you are having trouble with pregnancy or have had several miscarriages
- Treat scarring of tissues within the lining of the womb
- Place an intrauterine device, or coil, or remove a coil that has been displaced.
What Does the Procedure Involve?
Hysteroscopy is performed using a hysteroscope which is a thin, tube-like, lighted telescope. This hysteroscope is carefully inserted through the vaginal opening, up the cervix and into the womb. The doctor will then push a gas or fluid through the tube to inflate the womb to obtain a clear view of the insides. If this procedure is being done for surgery, surgical devices too will be inserted through the tube to perform the operation.
This procedure, for most diagnostic-only purposes, can be completed under local anaesthesia or General Anaesthesia(depending on the pain threshold of each patient). This procedure usually takes less than 10minutes.
General anaesthesia may be used if you are having a minor surgical procedure being carried out at the same time. This can take upto 30 minutes in total and will have to be performed at the hospital.
Recovery Period
Recovering from a hysteroscopy depends on the purpose of the procedure. If you have had a diagnostic hysteroscopy, you can return to your daily routine within a day. If you have had a treatment under general anaesthesia, like getting fibroids or polyps removed, then the recovery may take longer. However, there are certain symptoms that are common after a hysteroscopy:
- Stomach cramps
- Some bleeding
- Shoulder pain
- Nausea and dizziness
Your surgeon will guide you on post-operative precautions.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF