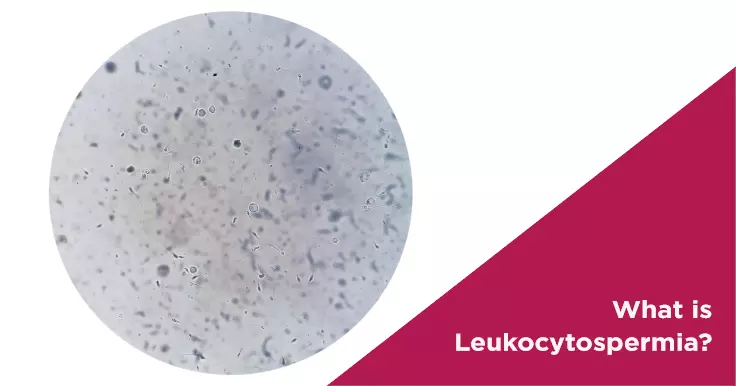
The high concentration of white blood cells can weaken sperm and damage genetic material by the release of reactive oxygen species. Leukocytospermia is not very common and affects less than 5% of infertile men.
Causes of Leukocytospermia
Leukocytospermia can be caused by many factors including:
- Inflammation
- Genital infections
- Autoimmune disorders
- Varicocele veins
- Narrowing of the urethra
- Systemic illnesses
- Consumption of alcohol, marijuana or smoking
- Infrequent ejaculation
The most common cause amongst the above is a genital infection caused by sexually transmitted microbes such as Chlamydia or other common microbes like Mycoplasma and E. coli. In some cases, men with this condition may not show any symptoms.
Diagnosis usually takes the form of urine tests to check for the presence of bacteria and other microorganisms that may trigger this condition. In rare cases, a semen culture may be required. If the test does have a positive result, you must abstain from sexual relations until the condition is treated and cured. This is because most of these infections can be sexually transmitted and may even cause permanent female infertility.
Treatment of Leukocytospermia
Treatment for this condition is aimed at removing white blood cells from semen. A course of antibiotics is a common form of treatment. This may be prescribed even if no bacteria are found in the urine test. Alternatively, NSAIDs may be prescribed to increase the sperm count. If the condition is caused by other underlying conditions such as a varicocele, surgery may be required to correct the varicocele. Other things that could help include:
- Quit alcohol, smoking and marijuana consumption
- Ejaculate more frequently
- Take antioxidant nutritional supplements
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF