Clinical vs Biochemical Pregnancy Loss
Some pregnancies may be terminated within the first few weeks of conception. In such cases, the pregnancy and the loss of the pregnancy can be detected only by a blood hormone test or a urine test. These are referred to as biochemical pregnancy losses. Biochemical pregnancy losses are not included when making a diagnosis for recurrent pregnancy losses.
By the 5th or 6th week of a pregnancy, the foetus should be visible on an ultrasound. Pregnancies that get terminated after this stage are termed as clinical pregnancy losses.
Causes of Recurrent Miscarriages
There are many factors that can contribute to having repeated miscarriages. Some can be controlled while others cannot. Below listed are some of the factors:
- Genetic
Missing chromosomes or the presence of an extra chromosome in the embryo are common causes for early miscarriages. Normally, a healthy embryo has 46 chromosomes. Chromosomal abnormalities often occur without any definite reason. These abnormalities do not allow the foetus to develop and hence lead to miscarriages. The risk of a miscarriage due to genetic abnormalities is usually higher for older women as compared to women under the age of 35 years. - Anatomic
An abnormally shaped uterus may cause a pregnancy loss. These anatomic abnormalities may be congenital or they may be the result of infections and previous surgeries. Other anatomic abnormalities that can contribute towards repeated miscarriages include the presence of a tissue band dividing the uterus and the presence of fibroids. - Lifestyle
Certain lifestyle habits such as smoking may cause miscarriages. The use of recreational drugs may also hinder a pregnancy. Other lifestyle issues that can cause a miscarriage include excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption and obesity. - Medical
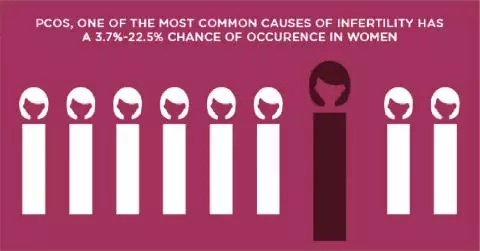
In some cases, underlying medical conditions such as polycystic ovarian syndrome, diabetes or thyroid disorders can trigger a miscarriage.
Along with the above, there are also many cases where an exact cause for the miscarriage cannot be identified.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF