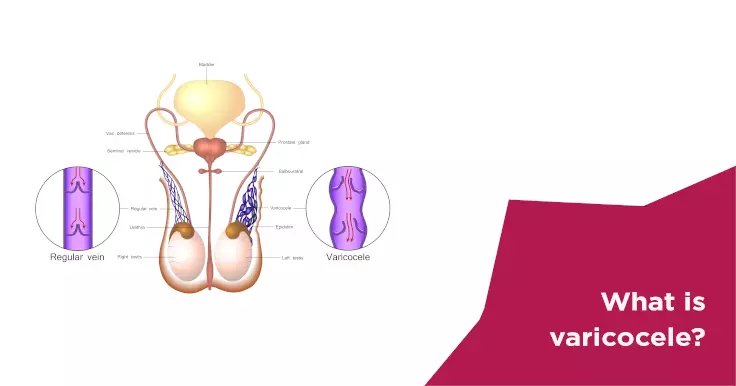
A varicocele is a group of enlarged veins in the scrotum, a skin-coloured sac which holds the testicles. The condition causes an obstacle in the flow of blood through the veins in that region. Although this condition may not cause severe symptoms, it can impact your fertility.
This is a comprehensive guide that explains varicocele’s meaning, and shares information about whether varicocele is dangerous or not, among other things.
Varicocele: What Is It?
A varicocele is an enlargement of veins inside the scrotum. The scrotum (a skin-covered sac that holds the testicles) contains the spermatic cord which houses several arteries and veins that maintain the blood flow to the reproductive glands. Abnormalities in those veins can cause the varicocele. The scrotum of a man affected with varicocele appears to be looking like a bag of worms. This condition occurs in about 1/6 men and is common in younger males of ages 15-25.
Varicocele although like varicose veins (which occurs in the legs), can only develop in the scrotum. A varicocele can lead to diminished sperm motility and quantity, which in turn can lead to infertility in men.
Usually, varicocele is harmless and not all of them need to be corrected with treatment. But if it causes infertility due to low sperm production or leads to some discomfort and pain, then its best to seek the help of a urologist for this problem.
Infertility due to varicocele is caused by an increased amount of blood in the scrotum which raises the temperature of the testicles. Sperms are best produced at a temperature lower than the body and varicocele deters that from happening.
Varicocele Causes
Even today doctors are uncertain about the causes of varicocele. However, it is theoretically believed to be formed due to some defect in the valves of the veins. These valves control the blood flow to and from the testicles. If due to some reasons there is an obstruction in the blood flow, then the blood backs up causing the veins to swell and enlarge.
Usually, this problem occurs during puberty when the testicles grow rapidly and need maximum blood flow. Varicocele leads to poor circulation, thus increasing the blood flow and the raising the temperature of the testicles. In some cases, this can hamper the sperm production or damage the already produced sperm leading to infertility. Also, varicocele is commonly seen on the left side of the testicles
Varicocele Symptoms
Some of the common varicocele symptoms are listed below:
- Swelling in the scrotum
- Dull pain in the testicles, that gets worse during the daytime especially in the hot weather or after some physical activities
- Heaviness felt in the testicles
- Lump in one of the testicles
- Twisted veins in the scrotum that looks like a bad of worms
- Shrunken testicles
- Symptoms of Varicocele
The varicocele symptoms can be categorised into 2 major categories as well:
1. Appearance of the Scrotum
Here are the symptoms that might help you recognise varicoceles by the look and feel of the scrotum:
a. Enlarged veins: A cluster of swollen veins may be visible in your scrotum, and they may look like a bag of worms.
b. Testicle size: One testicle may appear larger than the other. In this case, the scrotum affected with varicoceles will have the smaller testicle. Usually, the left scrotum develops varicoceles because of the arrangement of veins on that side.
c. Lump: If you feel a lump in your scrotum, you must visit your doctor immediately. It is important to note that if the lump is in fact varicoceles, then chances are that you will not feel any pain.
2. Pain in the Scrotum
Acute pain caused by varicoceles is not common. However, it can become painful if the veins are too enlarged, and the problem is not diagnosed soon enough. The pain might be continuous dull aching type or might worsen while standing/after exercise.
Varicocele complications
Varicocele can lead to difficulties in regulating the temperature of your testicles among other things. Additionally, oxidative stress and the buildup of toxins can occur in men who have varicocele. Such factors can lead to the following complications:
1. Infertility
Varicocele can lead to infertility in severe cases, which is far more serious than the above-mentioned ones. If you and your partner are unable to conceive due to low sperm count/motility, then varicoceles could be one factors that may be interfering with the process. The enlarged veins increase the temperature in that area and disallow smooth production of healthy sperms.
2. Poor testicular health
Boys who are going through puberty can experience troubles with testicle growth, hormone production, and other function of the testicles due to varicocele. If a man develops varicoceles, his testicles may shrink gradually due to the loss of tissue.
When to Seek Treatment for Varicocele?
There are certain varicoceles that can be left untreated as it does not cause any kind of harm or discomfort to the patient. However, if you experience pain or are not able to conceive due to low sperm count or motility, then your varicocele might need correction. If one finds the prevailing symptoms of this condition, it is always better to get it examined by a urologist as early as possible, who could help with the best treatment option available.
Varicocele Diagnosis
To diagnose varicocele, a physical examination will be done by your doctor. He will try to feel the veins by asking you to stand straight, taking a deep breath, and holding it while bearing down. In case of minor varicocele, if your doctor feels, the physical exam was not enough to be sure of it, then a scrotal ultrasound or thermography can also be done.
An ultrasound with veins that are wider than 3mm and the blood flowing in the wrong direction indicates that you might have varicoceles.
Varicocele Treatment Options
Generally, varicocele is not treated. But, if the affected person has some other problems like inability to father a child, pain or swelling in the scrotum, different size of testicles or lumps in the scrotum, then a proper treatment is required.
Treating varicoceles may not always be imperative. However, doctors may suggest medical treatment of varicoceles if you have the following symptoms:
- Pain
- Testicular atrophy
- Infertility due to low sperm count/motility
- Abnormal reports of semen analysis
Treatment should also be considered if you are thinking of assisted reproductive techniques, like IVF. Varicoceles treatments include:
1. Varicocelectomy (Conventional Open Surgery)
In this procedure, the surgeon accesses the affected area using ultrasound and surgical microscopes. The abnormal veins are then closed to reroute the blood through healthier veins to pump blood normally. This surgery is performed under local or general anaesthesia and the patient can go home the same day.
2. Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy Surgery
In this method, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen or upper thigh and enters the scrotum. Varicocele surgery is often recommended in teenage boys to treat varicocele; however, there is no guarantee for catch-up growth of testicles post-surgery.
3. Embolization
Percutaneous embolization is a varicocele treatment without surgery which can be done to shrink the varicocele. During this process, the doctor inserts either a tube down the neck or a catheter through the groin. Surgical tools are passed through these to block the veins by placing a coil in between them. This procedure can be done in the outpatient department itself and the recovery is very quick.
Varicocele’s Impact on Fertility
Although varicocele does not necessarily cause infertility, it is estimated that about 10-20% of men who are diagnosed with varicocele have trouble with fertility. Additionally, data suggests that about 40% of men who experience infertility have a varicocele. Varicocele can impact your fertility in the following ways:
- Decrease in the quality and quantity of sperm in addition to lower motility or movement and abnormal morphology shape
- Increased temperatures in the scrotum causes poor sperm production
Varicocele Prevention
Since there are any significant risk factors for varicoceles, it is difficult to prevent this condition. About 15 in every 100 men usually have varicoceles. Yet, there has been no linkage of increased or decreased risk of varicoceles with race, place of birth, or ethnicity of the male.
Tips on How to Manage Discomfort Caused by Varicocele
Anecdotal evidence suggests that you may benefit from the following if you have varicocele:
- Wear supportive underwear
- Lie down on your back and elevate your hips to ease the pain
- Consult with your doctor to take painkillers while you explore best treatment options
- Exercise in moderation regularly
- Try using a cold compress or ice wrapped in a towel to your scrotum
Recovery After Varicocele Treatment
Your varicoceles may resolve on their own over time. However, if the discomfort and pain persist making it difficult to go about your day, your doctor will suggest the best varicocele treatment for you. If you have gone through the surgery, which is quite common, you are likely to heal quickly with mild pain in the following days.
It is recommended that you avoid working out for at least 10-14 days after the surgery, but you can go back to work after a day or two of bed rest if your job does not involve any strenuous activity. In case you have undergone varicocele fertility treatment, your doctor will advise you to take a semen analysis done after 3-4 months of the procedure.
The healing time after an embolization is also relatively short and accompanied by mild pain only. Like a varicocelectomy, you are advised against working out for about 7-10 days after an embolization treatment as well.
The impact of varicocele treatment on fertility is unclear; some studies reveal that the man’s fertility improves after the treatment, while others indicate no significant difference in the man’s fertility after the treatment.
Latest Research and Developments:
Research is ongoing to understand this condition better. Here are a few resources to help you gather knowledge about this common condition:
- Varicocele by Urologic Clinics of North America provides an overview of the condition
- Varicocele: a bilateral disease by Fertility and Sterility shares insights about how men with varicocele were treated by embolization and the increase in their mean sperm concentration and pregnancy rates
- The varicocele diagnostic dilemmas, therapeutic challenges and future perspectives in the Asian Journal of Andrology sheds light on current treatment practices and difficulties in treating varicocele
- An update on the role of medical treatment including antioxidant therapy in varicocele in the Asian Journal of Andrology reveals that different varicocele medicine, including antioxidants, is being considered for better treatment options
- Treating varicocele in 2018: current knowledge and treatment options to get an idea about the latest therapies for varicocele treatment
- Pathophysiology and treatment options of varicocele: An overview in the Wiley Online Library reveals that antioxidants are promising medications for varicocele
FAQs About Varicocele
Q. Is it necessary for me to be treated for varicocele?
A. Generally, males don’t have any health problems if they develop varicocele. However, there is a significant percentage of males that can experience infertility caused by varicocele; such individuals are advised to seek treatment if they wish to father a child or if they are experiencing severe symptoms that is impacting their quality of life. Young adolescents with varicoceles are advised to get proper treatment as the condition can impact their testicular growth and health.
Q. How long does it take for the varicocele treatment to improve fertility?
A. There is no guarantee that varicocele treatment will improve your chances of successful conception. However, the recovery after surgical or minimally invasive treatment takes about 1-2 weeks. You can get a semen analysis done 3-4 months after the treatment to evaluate the result of the treatment.
Q. Should I worry if I have a lump in my scrotum?
A. Yes. If you find any abnormality in your scrotum or other body parts, it is advised that you consult a doctor. You may have varicocele, which is treatable condition, but you need to visit the doctor for accurate diagnosis.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF