Cervical Stenosis Risks and Potential Complications

Complications of Cervical Stenosis
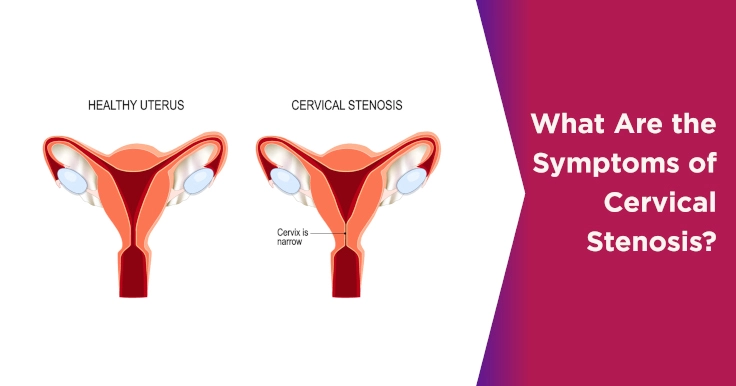
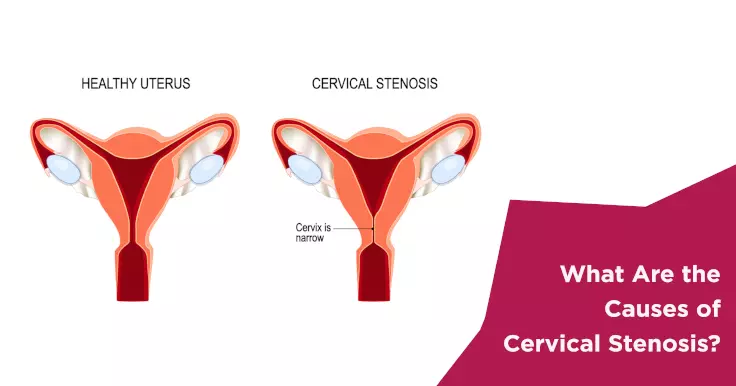
Cervical stenosis can be caused due to cancer of the cervix, infection in the uterus, surgeries such as endometrial ablation, or at times due to radiation therapy at the cervix area. There are a few risks of cervical stenosis that lead to certain complications in women which require good medical assistance.
Hematometra: In this condition, endometrial blood is retained inside the uterine cavity instead of flowing out through the vagina. Due to cervical stenosis, the blood is unable to reach the vaginal canal to exit the body and thus remains retained inside the uterus itself. Generally, in women, such an obstruction occurs due to issues with the cervix.
Pyometra: If instead of blood, pus or purulent material accumulates inside the uterine cavity, this condition is called pyometra. The condition mainly affects postmenopausal women and generally caused due to cervical stenosis or due to radiotherapy given to remove malignant lesions present in the genital tract.
Hydrometra: Instead of blood and pus, if fluid accumulates inside the uterus, this condition is called hydrometra.
Infertility: Cervical stenosis can make a woman infertile by obstructing sperm mobility since the passage to the uterus or fallopian tubes may be blocked by the cervix. Also, the cervical mucus that supports and protects the growing embryos, and also gives a lubricated medium for the sperm to swim into the body, is not sufficiently produced, due to which pregnancies may not last a full term.
How Cervical Stenosis Affects Fertility?
Cervical stenosis leads to the following issues in women which can directly or indirectly affect the fertility:
- No passage for sperms: A narrow cervix (or one which is completely closed) makes it extremely difficult for the sperm to swim through the reproductive tract and reach the fallopian tubes for fertilisation.
- Inflammation of uterus and endometriosis: When menstrual bleeding is completely blocked, the uterus gets filled with the menstrual blood which leads to pain and swelling of the uterus (hematometra). Sometimes, uterus is filled with pus and this condition is called pyometra. When endometrial cells grow and perish in other pelvic organs, this causes endometriosis.
- Less fertile cervical mucus: Cervical stenosis occurs due to scar tissues formed as a result of biopsy. The scar tissues hamper the production of cervical mucus, and this hinders the mobility and survival of the sperms.
- Fertility treatment complications: Intrauterine insemination and in vitro fertilisation can be done only by placing a catheter inside the cervix, and in either case when the opening of the cervix is too narrow, complications arise
- Risk of pregnancy loss or premature birth: Treatment for cervical stenosis weakens the cervix due to tissue damage and during pregnancy, this can make the cervix incompetent, that is cervix is not strong or closed enough to protect the growing embryo. This may cause pregnancy loss or premature birth of the baby.
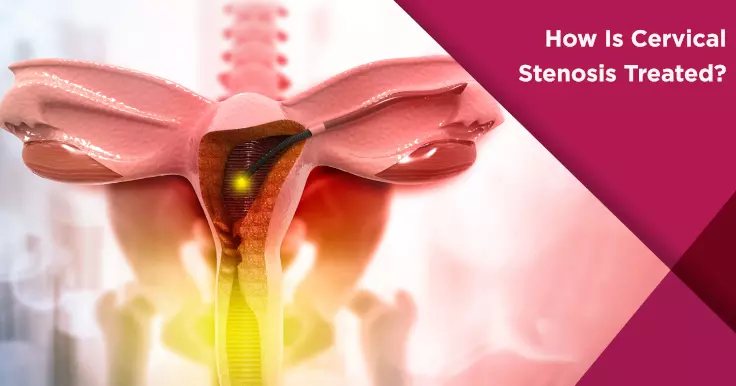
Physicians treat cervical stenosis by widening the cervix using dilators. At times, a cervical stent may also be inserted inside the cervix to prevent it from re-closing.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF